Service hotline:+86-(0)-18115476705
Antibody Application
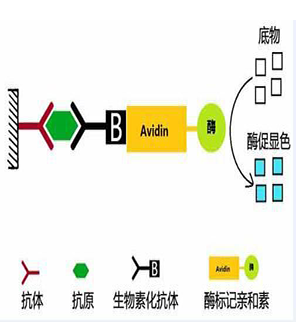
Principle of ELISA is based on the specific combination of antibody and antigen, ELISA can help us to make quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis. Couple target antibody and enzyme we want to analysis, colored substance will come into being after adding substrate into the enzyme; Antigen concentration of the sample will be known by inspecting its absorbance using spectrophotometer.
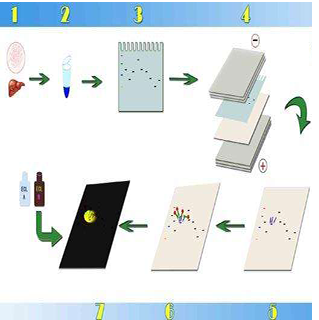
Western blotting uses specific antibodies to identify proteins that have been separated based on size by gel electrophoresis. The immunoassay uses a membrane made of nitrocellulose or PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride). The gel is placed next to the membrane and application of an electrical current induces the proteins to migrate from the gel to the membrane. The membrane can then be further processed with antibodies specific for the target of interest, and visualized using secondary antibodies and detection reagents.
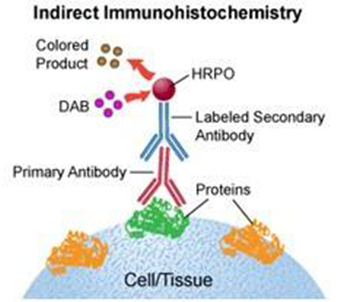
Immunohistochemical(IHC) staining is accomplished with antibodies that recognize the target antigen. Since antibodies are highly specific, the antibody will bind only to the antigen of interest in the tissue section. The antibody-antigen interaction is then visualized using either chromogenic detection, in which an enzyme conjugated to the antibody catalyzes the conversion of a substrate to produce a colored precipitate at the location of the antigen, or fluorescent detection, in which a fluorophore is conjugated to the antibody and can be visualized using fluorescence microscopy.
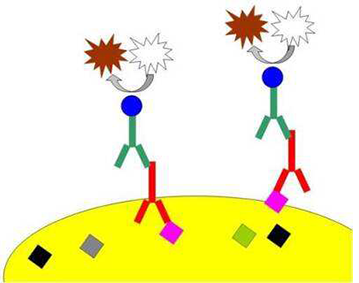
Immunocytochemistry or ICC is a technique that uses antibodies to visualize the localization of particular proteins within single cells. Compared to IHC, ICC provide higher space resolution.
Combine the antibody and protein in fixed cell culture, the mixed sample is visible because the antibody is fluorescence labeled, we can observe the signal using fluorescence microscope.
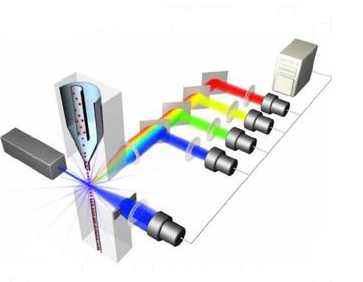
intracellular molecules, characterizing and defining different cell types in a heterogeneous cell population, assessing the purity of isolated subpopulations and analyzing cell size and volume. It allows simultaneous multi-parameter analysis of single cells.
The staining procedure involves making a single-cell suspension from cell culture or tissue samples. The cells are then incubated in tubes or microtiter plates with unlabeled or fluorochrome-labeled antibodies and analyzed on the flow cytometer.
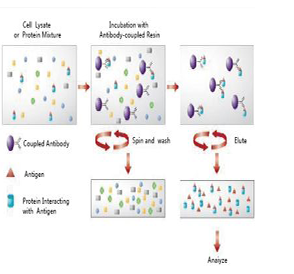
Immunoprecipitation is a method that enables the purification of a protein. An antibody for the protein of interest is incubated with a cell extract enabling the antibody to bind to the protein in solution. The antibody/antigen complex is then pulled out of the sample using protein A/G-coupled agarose beads. This isolates the protein of interest from the rest of the sample. The sample can then be separated by SDS-PAGE for western blot analysis.
ELISPOT, or enzyme linked immunospot, is a technique that was developed for the detection of secreted proteins, such as cytokines and growth factors. It is most commonly used in immunology research.
ELISPOT is performed using a PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane 96-well plate pre-coated with an antibody specific to the secreted protein. Cells are added to the plate and attach to the coated membrane. Cells are then stimulated and the secreted protein binds to the antibody. Next, a detection antibody is added that binds specifically to the bound protein.
Copyright © Nanjing TGpeptide Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.